There are countless discussions on artificial intelligence (AI), and ChatGPT is at the core of many of them. Supporters praise it as groundbreaking, while detractors claim it’s just an advanced algorithm. Is ChatGPT a True Artificial Intelligence-Let’s examine what constitutes “true AI” and how ChatGPT fits into it to cut through the clutter.
Identifying True AI: The Intelligence Standard
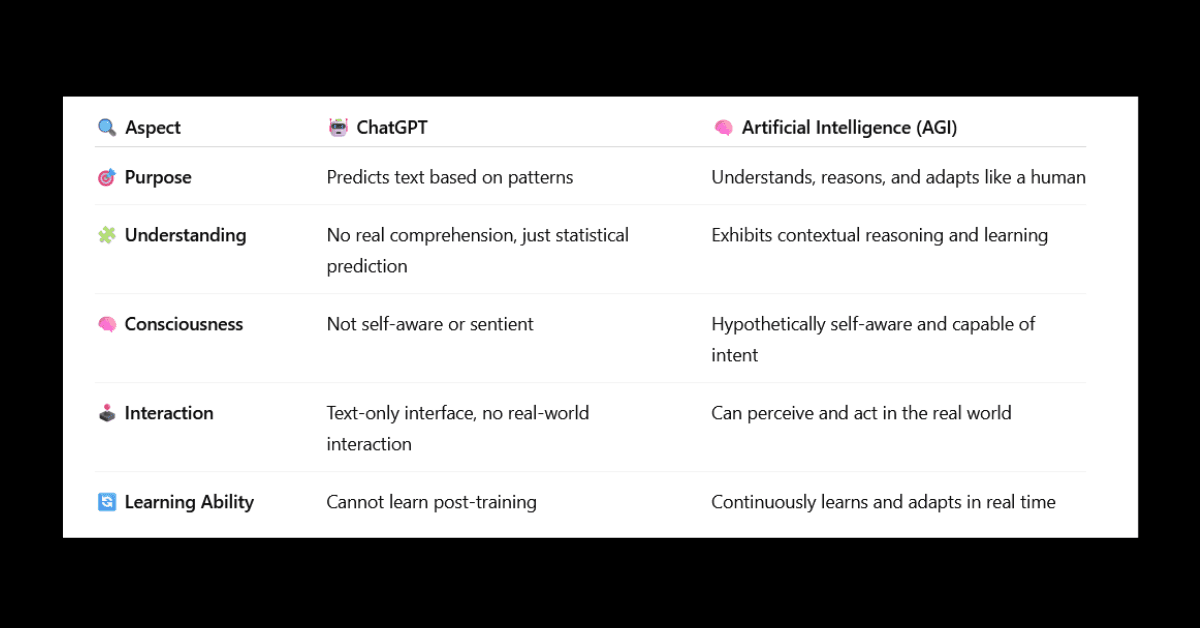
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), another name for true artificial intelligence, refers to a system that can reason, learn, and think like a person. AGI solves abstract issues, adapts to novel situations, and demonstrates self-awareness, in contrast to limited AI, which is superior at specialized tasks. For example, self-driving cars use limited AI, whereas AGI engages in philosophical debates and understands traffic regulations.
However, ChatGPT has very stringent guidelines. Instead of understanding concepts, it creates text by making predictions about sequences. The claim that it isn’t “real AI” is strengthened by this distinction. Let’s investigate further.
How ChatGPT Operates: Understanding Patterns-Is ChatGPT a True Artificial Intelligence
The transformer architecture, a neural network trained on enormous text datasets, is the foundation of ChatGPT. To forecast a sentence’s next word, it looks for statistical trends. Despite their apparent coherence, replies are the result of data correlations rather than comprehension. ChatGPT functions like having access to all the books in a library but not understanding their content.
The model is not conscious, curious, or intent. It mimics human speech based on training; it doesn’t “know” it’s responding to a query. This restriction sets it apart from contextual reasoning, which is the aim of AGI.
The Argument Against “True AI” in ChatGPT
Critics point out three main drawbacks:
Absence of Real-World Interaction: ChatGPT is unable to see or interact with the real world. It can comprehend text inputs, but unlike people or sophisticated robots, it is unable to learn from real-time sensory data.
Static Knowledge: It stops using training data in 2023. It is unable to learn from new events or update its knowledge on its own, unlike humans.
Lack of Intentionality: The system has no “intention” to accomplish objectives. It does not optimize for truth or problem-solving, but rather for content that sounds credible.
These discrepancies support claims that ChatGPT is a sophisticated tool rather than sentient intelligence.
The Rebuttal: The Hidden Potential of ChatGPT-Is ChatGPT a True Artificial Intelligence
Rejecting ChatGPT, according to its supporters, oversimplifies its accomplishments. It exhibits emergent behaviors beyond simple pattern-matching, yet is not AGI. For example:
Contextual Adaptation: It infers implicit user needs, modifies tone, and preserves discussion threads.
Cross-Domain Knowledge: It can handle a wide range of subjects without task-specific instruction, from poetry to code.
Creative Output: It produces what were long thought to be exclusively human characteristics, such as jokes, metaphors, and hypothetical situations.
These achievements make it difficult to distinguish between real cognitive flexibility and preprogrammed reactions.
The Training Paradox: Intelligence vs. Data-Is ChatGPT a True Artificial Intelligence
ChatGPT’s strength lies in its 45 terabytes of text data and 175 billion parameters. However, sheer scale is not the same as comprehension. A child learns “hot” with just one burn, whereas ChatGPT requires thousands of instances to learn well.
This “brute-force” method draws attention to a crucial AI discussion: Are human-like cognition and necessary to replicate human output? Not always. Grandmasters can be defeated by a chess AI that doesn’t comprehend strategy. In a similar vein, ChatGPT’s elegance conceals its mechanical essence.
Implications for Ethics: The Significance of the “True AI” Label
Referring to ChatGPT as “true AI” runs the danger of exaggerating its capabilities. Unaware of its limits, users may rely on it for emotional support or medical guidance. On the other hand, minimizing its effects overlooks dangers including prejudice, false information, and job displacement.
Openness is important. It is easier to control expectations when ChatGPT is framed as a tool rather than a sentient being. It is imperative that developers and policymakers work together to solve ethical issues without limiting creativity.
What ChatGPT Can Teach Us About the Path to AGI
Although ChatGPT is a first step, it is not AGI. To create better models in the future, researchers examine its shortcomings. For instance:
Hallucinations: ChatGPT exposes weaknesses in purely pattern-based learning when it fabricates facts.
Bias Amplification: Training on human data transmits human biases, highlighting the significance of ethical AI design.
The development of AGI is guided by these lessons, which highlight hybrid models that blend rule-based reasoning with data-driven learning.
Technical Reality vs. Public Perception
The media frequently portrays ChatGPT as “AI that thinks,” which fuels sci-fi imaginations. It is, in fact, a mirror reflecting human knowledge, imperfect as it may be. Non-technical listeners, who mistake fluency for comprehension, are perplexed by this discrepancy.
Users must be educated. Providing an explanation of ChatGPT’s technology encourages thoughtful conversations regarding its social function.

The Future: Overcoming the Divide Between AGI and ChatGPT
Future AI may combine robotics, sensory input, self-improvement algorithms, and ChatGPT’s linguistic abilities. AGI promises to create a system that can learn from mistakes, debate philosophy, and prepare meals.
ChatGPT continues to be a pioneer in narrow AI until then. It is evidence of human inventiveness rather than intellect per se.
Concluding Remarks: ChatGPT Is AI, But Not That AI.
Could ChatGPT be considered a real artificial intelligence? Yes—if we consider AI to be the ability of computers to execute tasks that call for human-like cognition. However, if we restrict the definition of “real AI” to entities that are sentient and self-aware, then the answer is no.
Definitions are the key to the solution. ChatGPT challenges our presumptions about intelligence, automates jobs, and transforms industries. However, it only hints at the potential of AGI. As we work toward the next innovation, we properly harness its potential by being aware of its advantages and disadvantages.
Let’s honor ChatGPT as a contemporary engineering wonder that advances our understanding of AGI without yet surpassing the threshold.
FAQ:
Are ChatGPT and AI the same?
- No, however, ChatGPT is classified as AI. ChatGPT focuses on language, whereas AI encompasses any systems that imitate human functions. Consider ChatGPT as one tool within the umbrella of AI.
Is ChatGPT an artificial general intelligence?
- No. It is not flexible or logical. AGI suggests thinking like humans, yet ChatGPT is pattern-oriented. But it does a good job of mimicking speech, giving the impression of more intellect.
What is artificial intelligence in ChatGPT?
- Here, AI refers to text creation based on patterns. ChatGPT predicts answers by analyzing data. ChatGPT does not “understand” content. Rather than mimicking human language cognitively, it does so statistically.
Is ChatGPT considered strong AI?
- No. Consciousness and learning are necessary for strong AI (AGI). Both are absent from ChatGPT. It is task-specific and has “weak AI.” Despite being sophisticated, it is unable to develop past its training.
Can ChatGPT be detected by AI?
- Yes, frequently. AI detectors identify recurring themes or strange wording. Updates, however, make it more difficult to differentiate outputs. Nevertheless, human assessment detects inconsistencies that technologies could overlook.



